Defence Sector Analysis: PSU vs Private Sector Growth
Comprehensive defence sector analysis with PSU vs private sector growth framework. Analyze HAL, BEL, L&T, Bharat Forge performance and investment opportunities in Indian defence sector.
Defence Sector Analysis: PSU vs Private Sector Growth
What You Can Do Next
- Read the full article for complete insights
- Save for later reference
- Share with others learning about this topic
Image not available
The Indian defence sector is undergoing a significant transformation with the government's Make in India initiative and increasing private sector participation. As we enter 2025, understanding the PSU vs private sector dynamics becomes crucial for investors. This comprehensive analysis examines the defence sector's growth prospects, company performance, and investment opportunities.
Defence Sector Overview 2025
Sector Characteristics
2025 Growth Outlook
PSU vs Private Sector Analysis
PSU Players
Private Sector Players
Company-Specific Analysis
HAL - The Aerospace Leader
BEL - The Electronics Leader
L&T - The Private Leader
Bharat Forge - The Manufacturing Leader
Make in India Impact
Government Initiatives
Private Sector Growth
Valuation Framework & Metrics
Valuation Metrics
Investment Framework
Investment Recommendations
Top Picks by Category
Risk Management
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key differences between PSU and private sector defence companies?
PSU companies have government backing, established relationships, and long-term contracts but face bureaucracy and limited innovation. Private sector companies offer innovation, efficiency, and global partnerships but have limited government contracts and face competition from PSUs. Both have their advantages and challenges.
What are the key growth drivers for defence sector in 2025?
Key growth drivers include Make in India initiative driving indigenous manufacturing, defence modernization and equipment upgradation, export opportunities and international partnerships, and growing private sector participation and investment. Government budget allocation for defence is also driving growth.
How to evaluate defence sector companies for investment?
Evaluate companies based on order book and pipeline, government relationships and contracts, technology capabilities and innovation, growth prospects and expansion plans, financial health and margins, and ESG practices and sustainability focus. Consider both fundamental analysis and technical analysis for better decision making.
What are the key risks in defence sector investments?
Key risks include government policy changes and budget cuts, intense competition and pricing pressure, technology disruption and obsolescence, regulatory challenges and compliance, and economic slowdown and reduced defence spending. Diversification and risk management are crucial.
How to value defence sector companies?
Use multiple valuation methods: P/E ratios (15-30x range), P/B ratios (2-5x range), EV/EBITDA (8-20x range), and DCF analysis considering growth prospects. Consider order book, government contracts, and competitive advantages. Focus on companies with strong fundamentals and growth prospects.
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as investment advice. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Please consult with a qualified financial advisor before making investment decisions. Defence sector investments are subject to market risks and government policy changes.
Continue Your Investment Journey
Discover more insights that match your interests

TCS Stock Analysis 2025: DCF Model and Growth Prospects
Complete fundamental analysis of TCS with DCF valuation model, growth prospects, and investment recommendation for 2025.

FMCG Sector Outlook 2025: Volume vs Value Growth
Comprehensive FMCG sector outlook for 2025 with volume vs value growth analysis. Analyze HUL, ITC, Nestle, Britannia performance and investment opportunities in Indian FMCG sector.

Crypto 2025: How Blockchain, AI, and Tokenization Are Shaping the Next Financial Revolution
Comprehensive analysis of crypto market trends for 2025, covering blockchain technology, AI integration, tokenization, and regulatory developments shaping the future of finance.
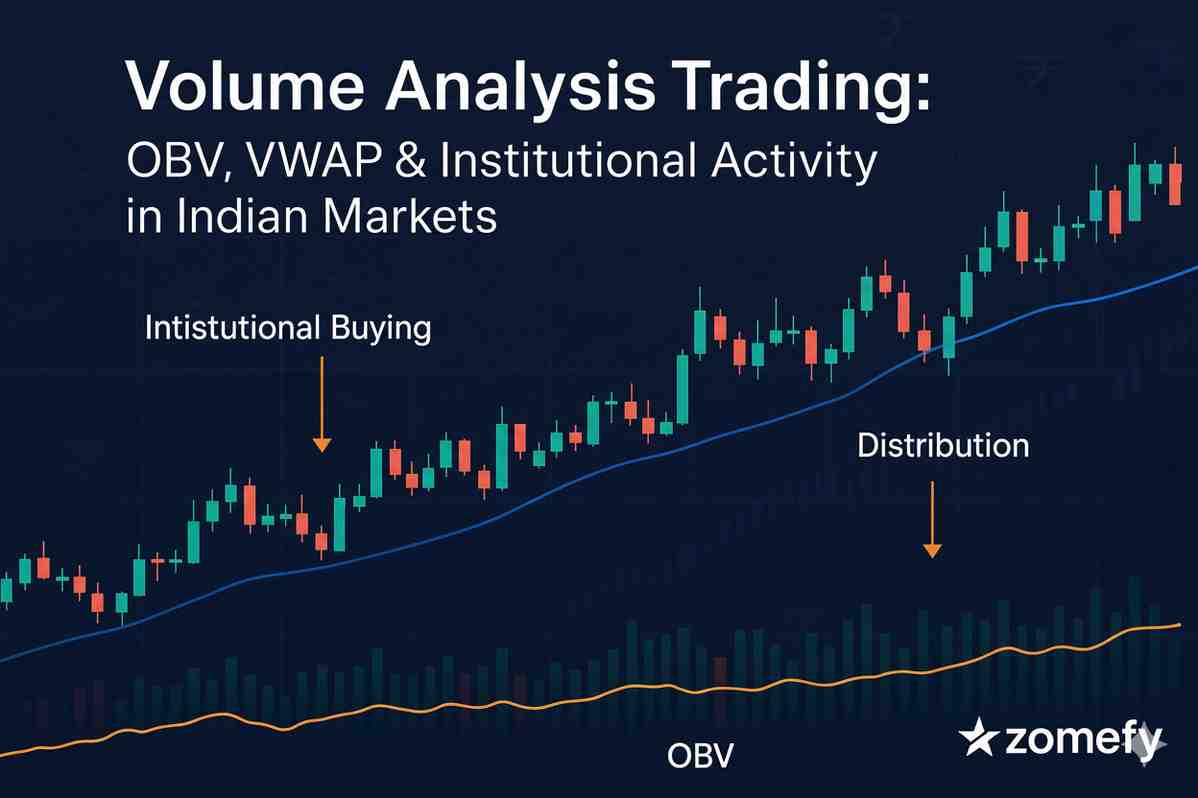
Volume Analysis Trading: OBV, VWAP & Institutional Activity in Indian Markets
Master volume analysis trading with OBV, VWAP, and institutional activity detection for Indian markets.
Explore More Insights
Continue your financial education journey
