Volume Analysis Trading: OBV, VWAP & Institutional Activity in Indian Markets
Master volume analysis trading with OBV, VWAP, and institutional activity detection for Indian markets. Learn to identify FII/DII activity and volume patterns using NSE stocks.
Volume Analysis Trading: OBV, VWAP & Institutional Activity in Indian Markets
What You Can Do Next
- Read the full article for complete insights
- Save for later reference
- Share with others learning about this topic
Image not available
Volume analysis is the backbone of professional trading, providing insights into institutional activity, market sentiment, and price movement validation. In Indian markets, where Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) and Domestic Institutional Investors (DIIs) play a crucial role, understanding volume patterns becomes essential for successful trading. This comprehensive guide covers On-Balance Volume (OBV), Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP), institutional activity detection, and advanced volume analysis techniques specifically tailored for NSE and BSE markets.
Understanding Volume Analysis
Volume Basics
Institutional Activity in Indian Markets
On-Balance Volume (OBV) Analysis
OBV Trading Strategies
OBV Divergence Patterns
Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP)
VWAP Trading Strategies
VWAP and Institutional Activity
Volume Pattern Analysis
Accumulation Patterns
Distribution Patterns
Volume Indicators and Oscillators
Accumulation/Distribution Line
Money Flow Index (MFI)
Advanced Volume Analysis
Volume Profile Analysis
Institutional Footprint Detection
Risk Management in Volume Trading
Volume-Based Risk Management
Avoiding False Signals
Conclusion
Continue Your Investment Journey
Discover more insights that match your interests

Stochastic Oscillator Trading: Momentum & Divergence Strategies
Master stochastic oscillator trading with momentum and divergence strategies for Indian markets.

Quantum Computing: The Next Frontier for Financial Security and Analytics
Discuss how emerging quantum technology may revolutionize risk modeling, transaction security, and investment strategies in global financial markets.

Support and Resistance Trading: Complete Strategy Guide for Indian Markets
Master support and resistance trading with horizontal levels, trendlines, and volume confirmation strategies for Indian markets.
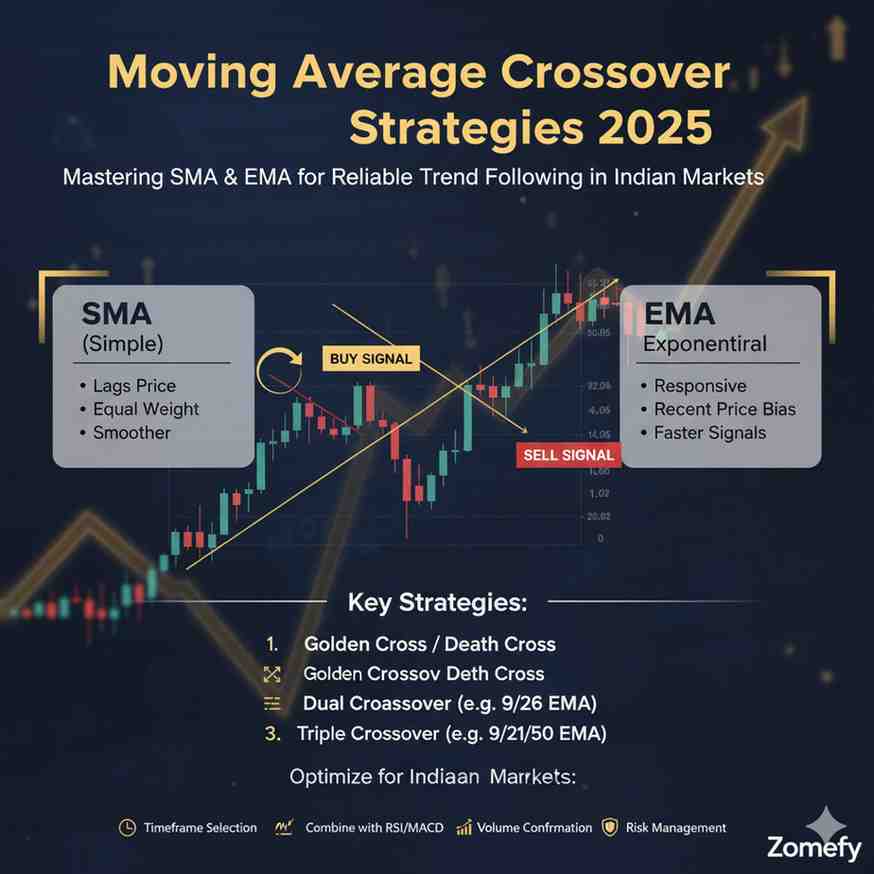
Moving Average Crossover Strategies 2025: Mastering SMA & EMA for Reliable Trend Following in Indian Markets
In the dynamic landscape of Indian financial markets, mastering technical tools for reliable trend identification is crucial for retail investors and financial professionals alike.
Explore More Insights
Continue your financial education journey
