Moving Average Trading: SMA, EMA & Crossover Strategies for Indian Stocks
Master moving average trading with SMA, EMA, and crossover strategies for Indian stocks. Learn golden cross, death cross, and 50/200 DMA strategies using NSE and BSE stocks.
Moving Average Trading: SMA, EMA & Crossover Strategies for Indian Stocks
What You Can Do Next
- Read the full article for complete insights
- Save for later reference
- Share with others learning about this topic
Image not available
Moving averages are among the most fundamental and widely used technical indicators in trading. They smooth out price data to identify trends and provide dynamic support and resistance levels. In Indian markets, moving averages are particularly effective due to the trending nature of NSE and BSE stocks. This comprehensive guide covers Simple Moving Averages (SMA), Exponential Moving Averages (EMA), crossover strategies, and advanced techniques specifically tailored for Indian market conditions.
Understanding Moving Averages
Simple Moving Average (SMA)
Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
Moving Average Crossover Strategies
Golden Cross Strategy
Death Cross Strategy
50/200 DMA Strategy
Uptrend Trading
Downtrend Trading
Multiple Moving Average Strategies
MA Alignment Strategy
MA Divergence Strategy
Moving Average as Support and Resistance
MA Support Trading
MA Resistance Trading
Advanced Moving Average Techniques
MA Confluence Analysis
MA Slope Analysis
Risk Management for MA Trading
Stop Loss Strategies
Target Setting Methods
Conclusion
Continue Your Investment Journey
Discover more insights that match your interests

How Gold Prices Have Moved Over the Last 100 Years (India & Global)
Comprehensive analysis of gold price movements over the last century in India and globally. Understand the forces that drive gold valuation and lessons for modern investors.
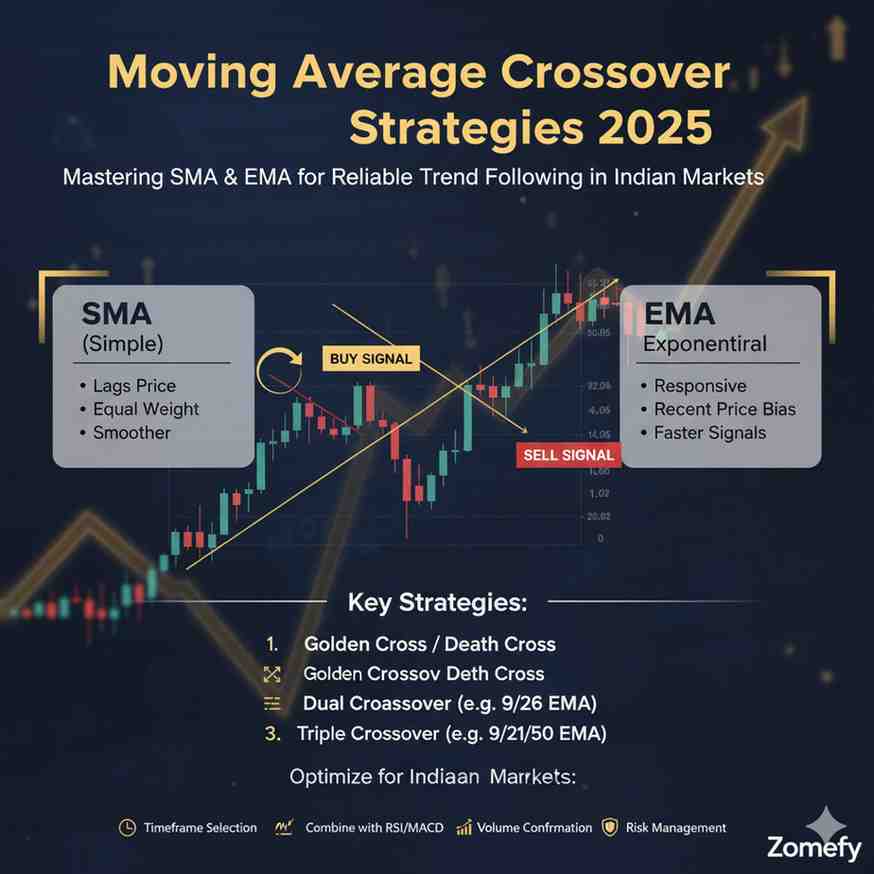
Moving Average Crossover Strategies 2025: Mastering SMA & EMA for Reliable Trend Following in Indian Markets
In the dynamic landscape of Indian financial markets, mastering technical tools for reliable trend identification is crucial for retail investors and financial professionals alike.

Risk Management for Technical Traders: Position Sizing & Stop-Loss Strategies
Master risk management for technical traders with position sizing, stop-loss strategies, and portfolio heat management.

Breakout Trading Strategy: Channel Breaks & Volume Confirmation
Master breakout trading with channel breaks, volume confirmation, and false breakout protection for Indian markets.
Explore More Insights
Continue your financial education journey
