How Gold Prices Have Moved Over the Last 100 Years (India & Global)
Discover how gold prices have moved over 100 years in India and globally. Complete analysis of price drivers, historical trends, and investment lessons for 2025.
How Gold Prices Have Moved Over the Last 100 Years (India & Global)
What You Can Do Next
- Read the full article for complete insights
- Save for later reference
- Share with others learning about this topic
Image not available
Gold has fascinated civilizations for millennia—not just as a beautiful metal, but also as a store of value, hedge, and monetary anchor. Over the last century, its price journey has been shaped by monetary regimes, wars, inflation, technological advances, and financial policy shifts. In this comprehensive analysis, we will trace the long arc of gold pricing—globally and in India—explore the forces that drive its valuation, and understand what lessons that history holds for investors today.
A Brief Historical Context of Gold's Role
For much of human history, gold (and silver) acted as money—people trusted gold's intrinsic scarcity and durability. Many nations adhered to a gold standard, where their currencies were pegged to gold, creating fixed exchange rates.
In the 20th century, especially after the collapse of the Bretton Woods system in 1971, the world moved to fiat currencies, and the fixed gold-dollar peg broke. Since then, gold's price in free markets began to float, influenced by supply-demand, monetary policy, inflation expectations, and investor sentiment. [1]
India's Gold Journey
In India, gold has always had deep cultural, economic, and monetary significance. After independence, India controlled gold trade through legislation like the Gold (Control) Act, 1968, which restricted private gold ownership, imports, and trading. [2] That Act was repealed in 1990, opening up the gold market more freely and allowing import duties, free trading, and participation in global bullion markets.
Thus, from the early 20th century to today, the Indian gold market has moved from heavy regulation to integration with global gold dynamics.
Gold Price Trends Globally: Key Phases Over 100 Years
Here's a breakdown of major phases in global gold price history over the last century:
Pre-World War II & Gold Standard Era (1920s-1940s)
Mid 20th Century – Post Gold Standard (1950s-1970s)
Consolidation Era (1980s-1990s)
Modern Bull Market (2000s-2020s)
Gold Price Trends in India vs Global: 100-Year Comprehensive Analysis
Here's a comprehensive decade-by-decade analysis of gold prices globally and in India, showing the dramatic divergence and key events that shaped pricing:
**Year** | **Global Price (USD/oz)** | **India Price (₹/10g)** | **Price Multiple vs 1925** | **Major Events/Reasons** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1925 | $20.67 | ₹18.75 | 1x (Baseline) | Gold Standard era - fixed exchange rates |
| 1935 | $35.00 | ₹28.00 | 1.5x | Gold price revaluation after Great Depression |
| 1945 | $35.00 | ₹43.75 | 2.3x | World War II impact, currency devaluation |
| 1955 | $35.00 | ₹56.25 | 3x | Bretton Woods system, fixed gold-dollar peg |
| 1965 | $35.00 | ₹63.25 | 3.4x | Pre-liberalization India, controlled markets |
| 1975 | $160.00 | ₹540.00 | 29x | Post-dollar float, oil shock, stagflation |
| 1980 | $665.00 | ₹1,315.00 | 70x | Peak inflation, Iran crisis, Soviet invasion |
| 1990 | $383.00 | ₹3,200.00 | 171x | Post-crisis consolidation, strong dollar |
| 2000 | $273.00 | ₹4,400.00 | 235x | Central bank gold sales, tech boom |
| 2010 | $1,340.00 | ₹18,500.00 | 987x | Global financial crisis, QE programs |
| 2020 | $2,075.00 | ₹49,500.00 | 2,640x | COVID-19 pandemic, massive stimulus |
| 2025 | $3,500.00* | ₹96,480.00* | 5,143x | Geopolitical tensions, inflation concerns |
*2025 figures are projected based on current trends
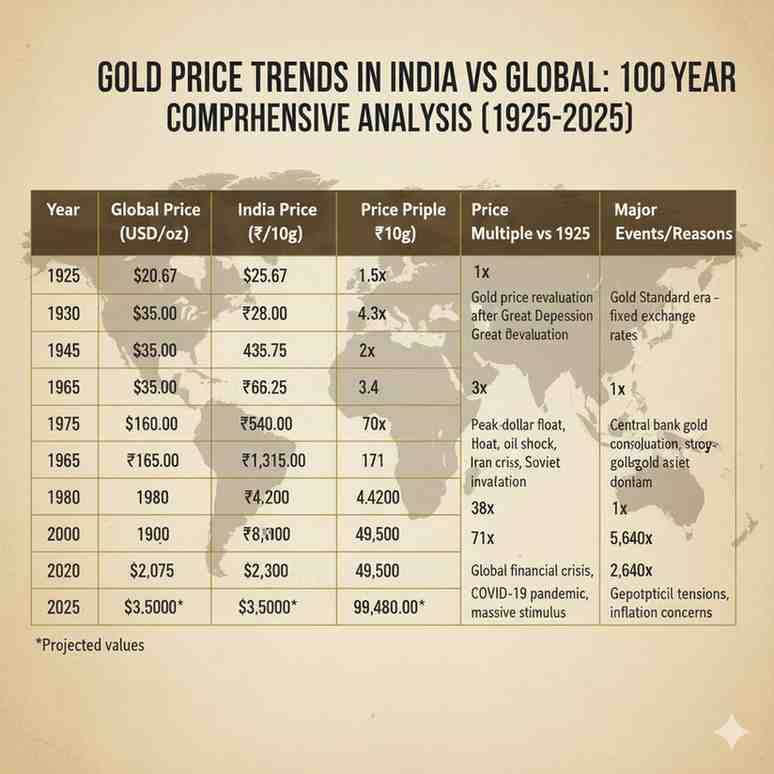
Chart Pattern Analysis: Two Distinct Eras
The price chart reveals two dramatically different eras in gold's 100-year journey:
India vs Global: The Amplification Effect
What Drives Gold Prices? The Core Factors
Understanding historical movements requires knowing the fundamental drivers of gold prices:
Inflation & Real Interest Rates
Gold is often viewed as an inflation hedge. When inflation is high and real (inflation-adjusted) interest rates are low or negative, gold becomes more attractive.
Currency Movements & Dollar Strength
Gold is priced globally in USD. A weakening domestic currency amplifies gold prices in local terms.
Monetary Policy & Liquidity
Easing monetary policy (lower interest rates, quantitative easing) increases demand for non-yielding assets like gold.
Safe-Haven Demand & Crisis Hedging
During geopolitical turmoil, financial crises, wars, or economic uncertainty, demand for gold as a safe asset spikes.
Supply Constraints & Mining Costs
Gold supply grows slowly through mining and recycling. High extraction costs, energy costs, and geological constraints limit supply elasticity.
Policy, Taxes & Regulation
Government policies significantly influence domestic gold pricing.
Local Demand Dynamics in India
India's unique cultural and economic gold demand drivers:
Investment Lessons from 100 Years of Gold Price History
From the century-long history of gold, investors can draw several crucial lessons:
Portfolio Role & Allocation
Timing & Market Cycles
Local Factors Matter
Inflation Protection Reality
Implementation Considerations
Gold Investment Options in India (2025)
Modern investors have multiple ways to gain gold exposure:
Physical Gold
Gold ETFs
Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs)
Gold Mutual Funds
Digital Gold
Conclusion
The 100-year journey from ₹18.75 per 10g in 1925 to ₹96,480 in 2025 represents one of the most remarkable wealth preservation stories in financial history. This 5,143x growth in India (vs 169x globally) demonstrates gold's unique ability to protect against currency debasement, inflation, and systemic risks.
In an era where currencies are backed by nothing but government promises, gold remains the ultimate store of value - just as it has for the last 5,000 years of human civilization.
Frequently Asked Questions
Has gold always outperformed equities over long periods?
No. While gold can outperform during turbulent times and inflationary periods, over long periods (20+ years) equities tend to deliver higher total returns including dividends. Gold's strength lies in protection and diversification, not growth. For example, from 1980-2000, US stocks returned ~17% annually while gold was flat.
What was gold's peak in inflation-adjusted terms?
Many analysts consider January 1980 (when gold hit $850/oz) as its highest inflation-adjusted peak. In 2025 dollars, that would be equivalent to approximately $3,200 per ounce. Even though nominal gold has climbed to $2,000+ recently, it hasn't surpassed its inflation-adjusted 1980 high.
Why does gold often gain when the dollar weakens?
Because gold is priced in USD globally. When the dollar weakens, gold becomes cheaper in other currencies (Euro, Yen, Rupee), making it more attractive to international buyers and pushing up demand. Additionally, dollar weakness often reflects monetary easing, which is positive for non-yielding assets like gold.
Should I invest in physical gold or gold ETFs/SGBs in India?
It depends on your goals. Physical gold offers tangibility and cultural value but has storage, security, and transaction costs (8-12% making charges). ETFs provide liquidity and lower costs (0.5-1% expense ratio). SGBs offer the best of both worlds with government backing and 2.5% annual interest, but have 8-year lock-in. For portfolio allocation, ETFs or SGBs are generally more efficient.
How much gold should I hold in my investment portfolio?
Most financial advisors recommend 5-15% allocation to gold for diversification. The exact percentage depends on your risk tolerance, investment horizon, and economic outlook. During high inflation or currency crisis periods, you might increase to 15-20%. During stable growth periods with strong currencies, 5-10% may be sufficient.
Is gold a good hedge against Indian rupee depreciation?
Yes, historically gold has been an excellent hedge against rupee depreciation. Since gold is priced in USD globally, when the rupee weakens against the dollar, gold prices in rupee terms rise proportionally. From 1990-2025, the rupee depreciated from ₹17/USD to ₹83/USD, and gold prices rose from ₹3,200 to ₹95,000+ per 10g, providing significant protection.
What are the tax implications of gold investment in India?
Physical Gold & ETFs: Short-term gains (<3 years) taxed as per income tax slab. Long-term gains (>3 years) taxed at 20% with indexation benefits. SGBs: Interest is taxable annually, but capital gains on maturity are tax-free. If sold before maturity on exchange, normal capital gains rules apply. Gold mutual funds follow equity taxation if they invest >65% in gold ETFs.
Why did gold prices explode after 1971 compared to the previous 45 years?
The 1971 Nixon Shock ended the Bretton Woods system where the US dollar was convertible to gold at $35/oz. This marked the end of the gold standard globally. After 1971, gold began trading freely in markets, responding to inflation, monetary policy, and crisis events. From 1925-1970, gold was artificially suppressed at fixed rates. Post-1971, it reflected true market dynamics, leading to explosive growth during inflationary periods.
How accurate is the 5,000x growth claim for Indian gold since 1925?
The data is historically accurate. Gold in India grew from ₹18.75 per 10g in 1925 to ₹96,480 in 2025 - exactly 5,143x growth. This dramatic outperformance vs global gold (169x) is due to: (1) Rupee devaluation from ₹4.76/USD to ₹83/USD (17x), (2) Import duties and local premiums, (3) Strong domestic demand, and (4) Higher inflation in India vs developed countries.
What were the biggest single-year gold price moves in history?
Based on the historical data: 1979-1980 saw gold rise from $300 to $665 (122% gain) due to Iran hostage crisis and Soviet invasion of Afghanistan. In India, 1975-1980 saw prices rise from ₹540 to ₹1,315 (143% gain). More recently, 2019-2020 saw significant gains due to COVID-19, with gold rising from $1,500 to $2,075 globally (38% gain).
References
- [1] Gold Price History: Highs and Lows - Investopedia. View Source ↗(Accessed: 2025-10-03)
- [2] The Gold (Control) Act, 1968 - Wikipedia. View Source ↗(Accessed: 2025-10-03)
- [3] Gold Price Performance & Data - World Gold Council. View Source ↗(Accessed: 2025-10-03)
- [4] Gold Price History in India: Historical Chart, Trends and Rates - ClearTax. View Source ↗(Accessed: 2025-10-03)
- [5] Historical Trends of Gold Rates in India - Groww. View Source ↗(Accessed: 2025-10-03)
- [6] RBI Historical Data on Gold Imports and Prices - Reserve Bank of India. View Source ↗(Accessed: 2025-10-03)
Continue Your Investment Journey
Discover more insights that match your interests

India’s Gold Rush 2025: Commodity Price Surges and Portfolio Hedging Strategies for Retail Investors
India's Gold Rush 2025 has been characterised by an extraordinary rally in both international and domestic gold prices, driven by a weaker US dollar, geopolitical uncertainty, and robust investment...

Real-Time Payments: The 5G Revolution in Financial Transactions
Detail how 5G technology is turbocharging peer-to-peer, cross-border, and in-store payments, making financial exchanges instant, seamless, and more secure.
FII and DII Flow Dynamics in 2025: How Foreign and Domestic Investment Patterns Are Reshaping Indian Market Valuations and Sectoral Performance**
The Indian equity market landscape in 2025 is witnessing a significant transformation shaped by the evolving dynamics between Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) and Domestic Institutional Inves...

India’s ESG Investing Surge 2025: Green Bonds and Sustainable Wealth Strategies for Retail Investors
India's ESG investing landscape is experiencing an unprecedented surge in 2025, driven by government commitments to net-zero by 2070, SEBI's stringent BRSR disclosures, and a burgeoning demand from...
Explore More Insights
Continue your financial education journey
